What is the KRAS-Variant
THE KRAS-VARIANT
What is the KRAS-Variant

Overview
The inherited KRAS-variant
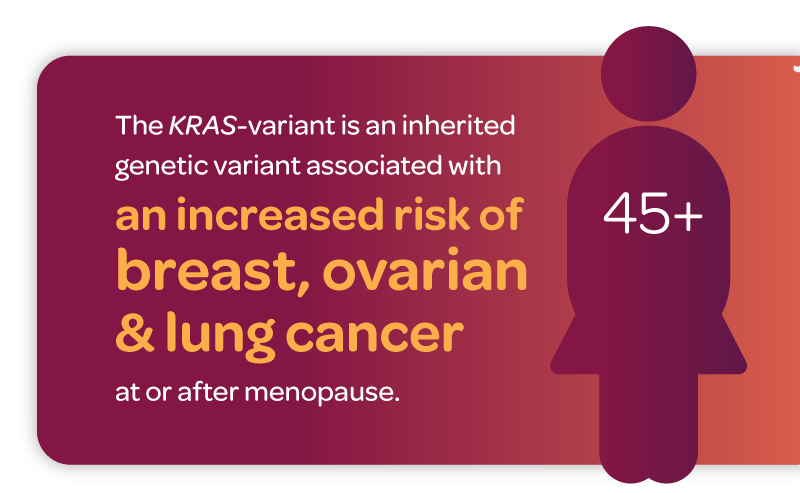
Discovered in 2006, the KRAS-variant is an inherited genetic variant associated with breast cancer,3 ovarian cancer,2 lung cancer,1 as well as other cancers,5,6 and the potential development of multiple cancers in the same individual.4,7
A genetic variant is a change in a specific part of the DNA in every cell of a person's body. Variants are not unusual and everyone has them. It is part of the reason no two people have the exact same DNA. Variants are not always beneficial, some can cause or increase your risk of disease.
Genetic variants come from your parents, whereas genetic mutations develop through everyday living. When a variant is inherited, that person will have it for life and may also pass it on to their children.
The KRAS-variant is NOT a KRAS mutation in a cancerous tumor
"KRAS mutations" have been found in different types of cancer tumors. Those KRAS mutations are not inherited, they occur in a KRAS gene during early cancer tumor development.45
In contrast, the KRAS-variant is inherited, something you have since birth and will continue to have throughout your life. You can learn more about the difference between the KRAS-variant and KRAS mutations here.
Understanding our terminology
Many sources, as we once did, use the term "mutation" to refer to any difference in a gene or genetic material, even those you were born with. However, since the term "mutation" can have a negative connotation, the genetics community and the American College of Genetics and Genomics have started replacing the term "mutation" with "variant." So while you will still see the term "mutation" used in other sources and our older publications for any genetic difference, we now use "variant" to refer to genetic differences a person is born with, and "mutation" only for genetic changes to cells after birth.

Hereditary Cancer
The significance of the KRAS-variant in hereditary cancers
The KRAS-variant is found in 6-10% of the population, and up to 25% of cancer patients. It is an example of a new type of biomarker that can explain the genetic cause of cancer for families with strong cancer histories.
The inherited KRAS-variant is far more common than previously known genetic variants associated with cancer, such as BRCA1, which is found in 0.25% of the overall population and 5-10% of breast and ovarian cancer patients. 17,18
What is a "biomarker"?
A biomarker is a biological molecule that is measurable by a clinician. They can be found in blood, body fluids, or tissues. By measuring the biomarkers in a person, a doctor can determine if that person is experiencing a physical ailment. Biomarkers can also be measured to determine the effectiveness of treatments for diseases or conditions.
While it had been believed that most cancer was due to chance, as only 5-10% of cancers had known hereditary causes,21 we have now found that more cancer risk is passed down from your parents due to inherited variants like the KRAS-variant.
Understanding of Cancer Causes
Before and after the KRAS-variant

Cancer that occurs without known family history or an inherited genetic difference.
Cancer caused by known inherited genetic variants such as BRCA or CHEK2.
Cancer that occurs in families more often than would be expected by chance, but there is no known genetic reason.

Led by Science
The scientific breakthrough that led to the discovery of a new type of inherited genetic variant
In your cells, your DNA is continuously making molecules (called RNA), which then make proteins. These proteins serve many vital functions in your body.19 However in recent years, scientists have discovered that DNA also makes certain forms of RNA that never turn into proteins. They are called non-coding RNA, and in general, this class of RNA is important in fetal development and continues to be important throughout your life to oversee and manage your response to stress and DNA damage in your body.20
This discovery has changed the fundamental understanding of human biology and has also led to new findings, like the inherited KRAS-variant.
Our work at MiraKind is to discover the genetic variants for many more cancers and to use this information to define the strategies and behaviors that may help reduce cancer risk for those who carry them, as well as to use these variants to help choose the safest cancer treatments when they are needed.

Personal Health
What the inherited KRAS-variant may mean for your health
Knowing you have this variant can guide you in lifestyle choices to help reduce your risk of developing cancer. You should also work with your doctor to discuss the need for increased screenings and the type of screenings.
If you have cancer already, knowing your KRAS-variant status will provide direction for you and your provider to determine the best treatments for you.
For Women
Estrogen and reducing cancer risk
A MiraKind study shows that women with the KRAS-variant can reduce cancer risk by maintaining their estrogen levels.7
Estrogen withdrawal occurs at menopause, after the removal of the ovaries, or after discontinuing hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
Unfortunately, HRT's use decreased dramatically after the 2002 Women's Health Initiative Study reported an association between HRT and worse health outcomes, including increased breast cancer risk.12
However, follow-up studies have indicated that for some women estrogen decreases breast cancer risk.46-49 For example in 2012, our founder Dr. Joanne Weidhaas led a study called "Hormones, the KRAS-variant and Breast Cancer Risk" that discovered estrogen plays a protective role against developing breast cancer in women with the KRAS-variant. Dr. Weidhaas explains these findings, in a webinar here.
The study's most important findings showed that for women with the KRAS-variant, estrogen withdrawal and lower estrogen levels were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing aggressive breast cancer - triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). These findings suggest that maintaining estrogen levels, through standard approaches such as hormone replacement therapy, could help prevent breast cancer in these women. This study was published in 2015 in the scientific article "Estrogen Withdrawal, Increased Breast Cancer Risk and the KRAS-variant."7
If you are peri-menopausal, or if you are considering a premenopausal oophorectomy, learning whether you have the inherited KRAS-variant can provide additional information to help you decide whether or not HRT is right for you.
Intensifying cancer screening
If you have the KRAS-variant, you have an increased risk of developing certain cancers, which can change how you and your doctor conduct proactive screening for them.
You may start screening earlier, screen more often, or even use different screening approaches. Catching any cancer in the earliest stages offers the greatest chance of cure.
You can find more information about screening for:
Cancer Patients
Treating specific cancers
Research has shown that the KRAS-variant also plays an important role in the body's response to cancer therapies.
Specifically, studies have found that certain cancer medications are far more effective for KRAS-variant cancer patients, while others are less effective. The difference in taking any cancer medication versus the best one for you, as a KRAS-variant patient, can lead to up to a 3-fold (300%) increase in your chance of survival.22,23
Research to determine which treatments work best for KRAS-variant patients have been conducted in breast,3 ovarian,22,25 colon,26-37 lung, and head and neck cancer.23,40,41 Here is a list of publications with findings about specific types of cancers.

Who should get tested for the inherited KRAS-variant?
If you have a family history of breast, ovarian, or lung cancer, or have a diagnosis of any type of cancer yourself, or are peri- or menopausal, you may want to be tested for the KRAS-variant.
Being tested for the inherited KRAS-variant provides information that you and your doctor can use to make better-informed decisions about your health.